nb module¶
Numba-compiled functions.
Provides an arsenal of Numba-compiled functions that are used for portfolio modeling, such as generating and filling orders. These only accept NumPy arrays and other Numba-compatible types.
Note
vectorbt treats matrices as first-class citizens and expects input arrays to be 2-dim, unless function has suffix _1d or is meant to be input to another function.
All functions passed as argument should be Numba-compiled.
Records should retain the order they were created in.
Warning
Accumulation of roundoff error possible. See here for explanation.
Rounding errors can cause trades and positions to not close properly:
>>> print('%.50f' % 0.1) # has positive error
0.10000000000000000555111512312578270211815834045410
>>> # many buy transactions with positive error -> cannot close position
>>> sum([0.1 for _ in range(1000000)]) - 100000
1.3328826753422618e-06
>>> print('%.50f' % 0.3) # has negative error
0.29999999999999998889776975374843459576368331909180
>>> # many sell transactions with negative error -> cannot close position
>>> 300000 - sum([0.3 for _ in range(1000000)])
5.657668225467205e-06
While vectorbt has implemented tolerance checks when comparing floats for equality, adding/subtracting small amounts large number of times may still introduce a noticable error that cannot be corrected post factum.
To mitigate this issue, avoid repeating lots of micro-transactions of the same sign. For example, reduce by np.inf or position_now to close a long/short position.
See vectorbt.utils.math_ for current tolerance values.
approx_order_value_nb function¶
approx_order_value_nb(
size,
size_type,
direction,
cash_now,
position_now,
free_cash_now,
val_price_now,
value_now
)
Approximate value of an order.
asset_flow_nb function¶
asset_flow_nb(
target_shape,
order_records,
col_map,
direction
)
Get asset flow series per column.
Returns the total transacted amount of assets at each time step.
asset_returns_nb function¶
asset_returns_nb(
cash_flow,
asset_value
)
Get asset return series per column/group.
asset_value_grouped_nb function¶
asset_value_grouped_nb(
asset_value,
group_lens
)
Get asset value series per group.
asset_value_nb function¶
asset_value_nb(
close,
assets
)
Get asset value series per column.
assets_nb function¶
assets_nb(
asset_flow
)
Get asset series per column.
Returns the current position at each time step.
benchmark_value_grouped_nb function¶
benchmark_value_grouped_nb(
close,
group_lens,
init_cash_grouped
)
Get market value per group.
benchmark_value_nb function¶
benchmark_value_nb(
close,
init_cash
)
Get market value per column.
build_call_seq function¶
build_call_seq(
target_shape,
group_lens,
call_seq_type=0
)
Not compiled but faster version of build_call_seq_nb().
build_call_seq_nb function¶
build_call_seq_nb(
target_shape,
group_lens,
call_seq_type=0
)
Build a new call sequence array.
buy_nb function¶
buy_nb(
exec_state,
size,
price,
direction=2,
fees=0.0,
fixed_fees=0.0,
slippage=0.0,
min_size=0.0,
max_size=inf,
size_granularity=nan,
lock_cash=False,
allow_partial=True,
percent=nan
)
Buy or/and cover.
cash_flow_grouped_nb function¶
cash_flow_grouped_nb(
cash_flow,
group_lens
)
Get cash flow series per group.
cash_flow_nb function¶
cash_flow_nb(
target_shape,
order_records,
col_map,
free
)
Get (free) cash flow series per column.
cash_grouped_nb function¶
cash_grouped_nb(
target_shape,
cash_flow_grouped,
group_lens,
init_cash_grouped
)
Get cash series per group.
cash_in_sim_order_nb function¶
cash_in_sim_order_nb(
cash_flow,
group_lens,
init_cash_grouped,
call_seq
)
Get cash series in simulation order.
cash_nb function¶
cash_nb(
cash_flow,
init_cash
)
Get cash series per column.
check_group_init_cash_nb function¶
check_group_init_cash_nb(
group_lens,
n_cols,
init_cash,
cash_sharing
)
Check init_cash.
check_group_lens_nb function¶
check_group_lens_nb(
group_lens,
n_cols
)
Check group_lens.
close_position_nb function¶
close_position_nb(
price=inf,
fees=0.0,
fixed_fees=0.0,
slippage=0.0,
min_size=0.0,
max_size=inf,
size_granularity=nan,
reject_prob=0.0,
lock_cash=False,
allow_partial=True,
raise_reject=False,
log=False
)
Close the current position.
copy_trade_record_nb function¶
copy_trade_record_nb(
record,
trade_record
)
Copy a trade record.
dir_enex_signal_func_nb function¶
dir_enex_signal_func_nb(
c,
entries,
exits,
direction
)
Resolve direction-aware signals out of entries, exits, and direction.
execute_order_nb function¶
execute_order_nb(
state,
order
)
Execute an order given the current state.
Args
state:ProcessOrderState- See ProcessOrderState.
order:Order- See Order.
Error is thrown if an input has value that is not expected. Order is ignored if its execution has no effect on current balance. Order is rejected if an input goes over a limit/restriction.
fill_entry_trades_in_position_nb function¶
fill_entry_trades_in_position_nb(
order_records,
col_map,
col,
first_c,
last_c,
first_entry_size,
first_entry_fees,
exit_idx,
exit_size_sum,
exit_gross_sum,
exit_fees_sum,
direction,
status,
parent_id,
trade_records,
tidx
)
Fill entry trades located within a single position.
fill_log_record_nb function¶
fill_log_record_nb(
record,
record_id,
i,
col,
group,
cash,
position,
debt,
free_cash,
val_price,
value,
order,
new_cash,
new_position,
new_debt,
new_free_cash,
new_val_price,
new_value,
order_result,
order_id
)
Fill a log record.
fill_order_record_nb function¶
fill_order_record_nb(
record,
record_id,
i,
col,
order_result
)
Fill an order record.
fill_position_record_nb function¶
fill_position_record_nb(
record,
id_,
trade_records
)
Fill a position record by aggregating trade records.
fill_trade_record_nb function¶
fill_trade_record_nb(
record,
id_,
col,
size,
entry_idx,
entry_price,
entry_fees,
exit_idx,
exit_price,
exit_fees,
direction,
status,
parent_id
)
Fill a trade record.
final_value_nb function¶
final_value_nb(
total_profit,
init_cash
)
Get total profit per column/group.
flex_simulate_nb function¶
flex_simulate_nb(
target_shape,
group_lens,
init_cash,
cash_sharing,
segment_mask=array(True),
call_pre_segment=False,
call_post_segment=False,
pre_sim_func_nb=no_pre_func_nb,
pre_sim_args=(),
post_sim_func_nb=no_post_func_nb,
post_sim_args=(),
pre_group_func_nb=no_pre_func_nb,
pre_group_args=(),
post_group_func_nb=no_post_func_nb,
post_group_args=(),
pre_segment_func_nb=no_pre_func_nb,
pre_segment_args=(),
post_segment_func_nb=no_post_func_nb,
post_segment_args=(),
flex_order_func_nb=no_flex_order_func_nb,
flex_order_args=(),
post_order_func_nb=no_post_func_nb,
post_order_args=(),
close=array(nan),
ffill_val_price=True,
update_value=False,
fill_pos_record=True,
max_orders=None,
max_logs=0,
flex_2d=True
)
Same as simulate_nb(), but with no predefined call sequence.
In contrast to order_func_nb insimulate_nb(), post_order_func_nb is a segment-level order function that returns a column along with the order, and gets repeatedly called until some condition is met. This allows multiple orders to be issued within a single element and in an arbitrary order.
The order function should accept FlexOrderContext, unpacked tuple from pre_segment_func_nb, and *flex_order_args. Should return column and Order. To break out of the loop, return column of -1.
Note
Since one element can now accommodate multiple orders, you may run into "order_records index out of range" exception. In this case, you should increase max_orders. This cannot be done automatically and dynamically to avoid performance degradation.
Usage
- The same example as in simulate_nb():
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from numba import njit
>>> from vectorbt.portfolio.enums import SizeType, Direction
>>> from vectorbt.portfolio.nb import (
... get_col_elem_nb,
... order_nb,
... order_nothing_nb,
... flex_simulate_nb,
... flex_simulate_row_wise_nb,
... sort_call_seq_out_nb
... )
>>> @njit
... def pre_sim_func_nb(c):
... print('before simulation')
... return ()
>>> @njit
... def pre_group_func_nb(c):
... print('\tbefore group', c.group)
... # Create temporary arrays and pass them down the stack
... order_value_out = np.empty(c.group_len, dtype=np.float64)
... call_seq_out = np.empty(c.group_len, dtype=np.int64)
... # Forward down the stack
... return (order_value_out, call_seq_out)
>>> @njit
... def pre_segment_func_nb(c, order_value_out, call_seq_out, size, price, size_type, direction):
... print('\t\tbefore segment', c.i)
... for col in range(c.from_col, c.to_col):
... # Here we use order price for group valuation
... c.last_val_price[col] = get_col_elem_nb(c, col, price)
...
... # Same as for simulate_nb, but since we don't have a predefined c.call_seq_now anymore,
... # we need to store our new call sequence somewhere else
... call_seq_out[:] = np.arange(c.group_len)
... sort_call_seq_out_nb(c, size, size_type, direction, order_value_out, call_seq_out)
...
... # Forward the sorted call sequence
... return (call_seq_out,)
>>> @njit
... def flex_order_func_nb(c, call_seq_out, size, price, size_type, direction, fees, fixed_fees, slippage):
... if c.call_idx < c.group_len:
... col = c.from_col + call_seq_out[c.call_idx]
... print('\t\t\tcreating order', c.call_idx, 'at column', col)
... # # Create and return an order
... return col, order_nb(
... size=get_col_elem_nb(c, col, size),
... price=get_col_elem_nb(c, col, price),
... size_type=get_col_elem_nb(c, col, size_type),
... direction=get_col_elem_nb(c, col, direction),
... fees=get_col_elem_nb(c, col, fees),
... fixed_fees=get_col_elem_nb(c, col, fixed_fees),
... slippage=get_col_elem_nb(c, col, slippage)
... )
... # All columns already processed -> break the loop
... print('\t\t\tbreaking out of the loop')
... return -1, order_nothing_nb()
>>> @njit
... def post_order_func_nb(c, call_seq_out):
... print('\t\t\t\torder status:', c.order_result.status)
... return None
>>> @njit
... def post_segment_func_nb(c, order_value_out, call_seq_out):
... print('\t\tafter segment', c.i)
... return None
>>> @njit
... def post_group_func_nb(c):
... print('\tafter group', c.group)
... return None
>>> @njit
... def post_sim_func_nb(c):
... print('after simulation')
... return None
>>> target_shape = (5, 3)
>>> np.random.seed(42)
>>> group_lens = np.array([3]) # one group of three columns
>>> init_cash = np.array([100.]) # one capital per group
>>> cash_sharing = True
>>> call_seq = build_call_seq(target_shape, group_lens) # will be overridden
>>> segment_mask = np.array([True, False, True, False, True])[:, None]
>>> segment_mask = np.copy(np.broadcast_to(segment_mask, target_shape))
>>> size = np.asarray(1 / target_shape[1]) # scalars must become 0-dim arrays
>>> price = close = np.random.uniform(1, 10, size=target_shape)
>>> size_type = np.asarray(SizeType.TargetPercent)
>>> direction = np.asarray(Direction.LongOnly)
>>> fees = np.asarray(0.001)
>>> fixed_fees = np.asarray(1.)
>>> slippage = np.asarray(0.001)
>>> order_records, log_records = flex_simulate_nb(
... target_shape,
... group_lens,
... init_cash,
... cash_sharing,
... segment_mask=segment_mask,
... pre_sim_func_nb=pre_sim_func_nb,
... post_sim_func_nb=post_sim_func_nb,
... pre_group_func_nb=pre_group_func_nb,
... post_group_func_nb=post_group_func_nb,
... pre_segment_func_nb=pre_segment_func_nb,
... pre_segment_args=(size, price, size_type, direction),
... post_segment_func_nb=post_segment_func_nb,
... flex_order_func_nb=flex_order_func_nb,
... flex_order_args=(size, price, size_type, direction, fees, fixed_fees, slippage),
... post_order_func_nb=post_order_func_nb
... )
before simulation
before group 0
before segment 0
creating order 0 at column 0
order status: 0
creating order 1 at column 1
order status: 0
creating order 2 at column 2
order status: 0
breaking out of the loop
after segment 0
before segment 2
creating order 0 at column 1
order status: 0
creating order 1 at column 2
order status: 0
creating order 2 at column 0
order status: 0
breaking out of the loop
after segment 2
before segment 4
creating order 0 at column 0
order status: 0
creating order 1 at column 2
order status: 0
creating order 2 at column 1
order status: 0
breaking out of the loop
after segment 4
after group 0
after simulation
flex_simulate_row_wise_nb function¶
flex_simulate_row_wise_nb(
target_shape,
group_lens,
init_cash,
cash_sharing,
segment_mask=array(True),
call_pre_segment=False,
call_post_segment=False,
pre_sim_func_nb=no_pre_func_nb,
pre_sim_args=(),
post_sim_func_nb=no_post_func_nb,
post_sim_args=(),
pre_row_func_nb=no_pre_func_nb,
pre_row_args=(),
post_row_func_nb=no_post_func_nb,
post_row_args=(),
pre_segment_func_nb=no_pre_func_nb,
pre_segment_args=(),
post_segment_func_nb=no_post_func_nb,
post_segment_args=(),
flex_order_func_nb=no_flex_order_func_nb,
flex_order_args=(),
post_order_func_nb=no_post_func_nb,
post_order_args=(),
close=array(nan),
ffill_val_price=True,
update_value=False,
fill_pos_record=True,
max_orders=None,
max_logs=0,
flex_2d=True
)
Same as flex_simulate_nb(), but iterates using row-major order, with the rows changing fastest, and the columns/groups changing slowest.
generate_stop_signal_nb function¶
generate_stop_signal_nb(
position_now,
upon_stop_exit,
accumulate
)
Generate stop signal and change accumulation if needed.
get_col_elem_nb function¶
get_col_elem_nb(
ctx,
col,
a
)
Get the current element using flexible indexing given the context and the column.
get_elem_nb function¶
get_elem_nb(
ctx,
a
)
Get the current element using flexible indexing given just the context.
get_entry_trades_nb function¶
get_entry_trades_nb(
order_records,
close,
col_map
)
Fill entry trade records by aggregating order records.
Entry trade records are buy orders in a long position and sell orders in a short position.
Usage
>>> import numpy as np
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> from numba import njit
>>> from vectorbt.records.nb import col_map_nb
>>> from vectorbt.portfolio.nb import simulate_from_orders_nb, get_entry_trades_nb
>>> close = order_price = np.array([
... [1, 6],
... [2, 5],
... [3, 4],
... [4, 3],
... [5, 2],
... [6, 1]
... ])
>>> size = np.asarray([
... [1, -1],
... [0.1, -0.1],
... [-1, 1],
... [-0.1, 0.1],
... [1, -1],
... [-2, 2]
... ])
>>> target_shape = close.shape
>>> group_lens = np.full(target_shape[1], 1)
>>> init_cash = np.full(target_shape[1], 100)
>>> call_seq = np.full(target_shape, 0)
>>> order_records, log_records = simulate_from_orders_nb(
... target_shape,
... group_lens,
... init_cash,
... call_seq,
... size=size,
... price=close,
... fees=np.asarray(0.01),
... slippage=np.asarray(0.01)
... )
>>> col_map = col_map_nb(order_records['col'], target_shape[1])
>>> entry_trade_records = get_entry_trades_nb(order_records, close, col_map)
>>> pd.DataFrame.from_records(entry_trade_records)
id col size entry_idx entry_price entry_fees exit_idx exit_price \
0 0 0 1.0 0 1.01 0.01010 3 3.060000
1 1 0 0.1 1 2.02 0.00202 3 3.060000
2 2 0 1.0 4 5.05 0.05050 5 5.940000
3 3 0 1.0 5 5.94 0.05940 5 6.000000
4 4 1 1.0 0 5.94 0.05940 3 3.948182
5 5 1 0.1 1 4.95 0.00495 3 3.948182
6 6 1 1.0 4 1.98 0.01980 5 1.010000
7 7 1 1.0 5 1.01 0.01010 5 1.000000
exit_fees pnl return direction status parent_id
0 0.030600 2.009300 1.989406 0 1 0
1 0.003060 0.098920 0.489703 0 1 0
2 0.059400 0.780100 0.154475 0 1 1
3 0.000000 -0.119400 -0.020101 1 0 2
4 0.039482 1.892936 0.318676 1 1 3
5 0.003948 0.091284 0.184411 1 1 3
6 0.010100 0.940100 0.474798 1 1 4
7 0.000000 -0.020100 -0.019901 0 0 5
get_exit_trades_nb function¶
get_exit_trades_nb(
order_records,
close,
col_map
)
Fill exit trade records by aggregating order records.
Exit trade records are sell orders in a long position and buy orders in a short position.
Usage
>>> import numpy as np
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> from numba import njit
>>> from vectorbt.records.nb import col_map_nb
>>> from vectorbt.portfolio.nb import simulate_from_orders_nb, get_exit_trades_nb
>>> close = order_price = np.array([
... [1, 6],
... [2, 5],
... [3, 4],
... [4, 3],
... [5, 2],
... [6, 1]
... ])
>>> size = np.asarray([
... [1, -1],
... [0.1, -0.1],
... [-1, 1],
... [-0.1, 0.1],
... [1, -1],
... [-2, 2]
... ])
>>> target_shape = close.shape
>>> group_lens = np.full(target_shape[1], 1)
>>> init_cash = np.full(target_shape[1], 100)
>>> call_seq = np.full(target_shape, 0)
>>> order_records, log_records = simulate_from_orders_nb(
... target_shape,
... group_lens,
... init_cash,
... call_seq,
... size=size,
... price=close,
... fees=np.asarray(0.01),
... slippage=np.asarray(0.01)
... )
>>> col_map = col_map_nb(order_records['col'], target_shape[1])
>>> exit_trade_records = get_exit_trades_nb(order_records, close, col_map)
>>> pd.DataFrame.from_records(exit_trade_records)
id col size entry_idx entry_price entry_fees exit_idx exit_price \
0 0 0 1.0 0 1.101818 0.011018 2 2.97
1 1 0 0.1 0 1.101818 0.001102 3 3.96
2 2 0 1.0 4 5.050000 0.050500 5 5.94
3 3 0 1.0 5 5.940000 0.059400 5 6.00
4 4 1 1.0 0 5.850000 0.058500 2 4.04
5 5 1 0.1 0 5.850000 0.005850 3 3.03
6 6 1 1.0 4 1.980000 0.019800 5 1.01
7 7 1 1.0 5 1.010000 0.010100 5 1.00
exit_fees pnl return direction status parent_id
0 0.02970 1.827464 1.658589 0 1 0
1 0.00396 0.280756 2.548119 0 1 0
2 0.05940 0.780100 0.154475 0 1 1
3 0.00000 -0.119400 -0.020101 1 0 2
4 0.04040 1.711100 0.292496 1 1 3
5 0.00303 0.273120 0.466872 1 1 3
6 0.01010 0.940100 0.474798 1 1 4
7 0.00000 -0.020100 -0.019901 0 0 5
get_free_cash_diff_nb function¶
get_free_cash_diff_nb(
position_before,
position_now,
debt_now,
price,
fees
)
Get updated debt and free cash flow.
get_group_value_ctx_nb function¶
get_group_value_ctx_nb(
seg_ctx
)
Get group value from context.
Accepts SegmentContext.
Best called once from pre_segment_func_nb. To set the valuation price, change last_val_price of the context in-place.
Note
Cash sharing must be enabled.
get_group_value_nb function¶
get_group_value_nb(
from_col,
to_col,
cash_now,
last_position,
last_val_price
)
Get group value.
get_long_size_nb function¶
get_long_size_nb(
position_before,
position_now
)
Get long size.
get_positions_nb function¶
get_positions_nb(
trade_records,
col_map
)
Fill position records by aggregating trade records.
Trades can be entry trades, exit trades, and even positions themselves - all will produce the same results.
Usage
- Building upon the example in get_exit_trades_nb():
>>> from vectorbt.portfolio.nb import get_positions_nb
>>> col_map = col_map_nb(exit_trade_records['col'], target_shape[1])
>>> position_records = get_positions_nb(exit_trade_records, col_map)
>>> pd.DataFrame.from_records(position_records)
id col size entry_idx entry_price entry_fees exit_idx exit_price \
0 0 0 1.1 0 1.101818 0.01212 3 3.060000
1 1 0 1.0 4 5.050000 0.05050 5 5.940000
2 2 0 1.0 5 5.940000 0.05940 5 6.000000
3 3 1 1.1 0 5.850000 0.06435 3 3.948182
4 4 1 1.0 4 1.980000 0.01980 5 1.010000
5 5 1 1.0 5 1.010000 0.01010 5 1.000000
exit_fees pnl return direction status parent_id
0 0.03366 2.10822 1.739455 0 1 0
1 0.05940 0.78010 0.154475 0 1 1
2 0.00000 -0.11940 -0.020101 1 0 2
3 0.04343 1.98422 0.308348 1 1 3
4 0.01010 0.94010 0.474798 1 1 4
5 0.00000 -0.02010 -0.019901 0 0 5
get_short_size_nb function¶
get_short_size_nb(
position_before,
position_now
)
Get short size.
get_stop_price_nb function¶
get_stop_price_nb(
position_now,
stop_price,
stop,
open,
low,
high,
hit_below
)
Get stop price.
If hit before open, returns open.
get_trade_stats_nb function¶
get_trade_stats_nb(
size,
entry_price,
entry_fees,
exit_price,
exit_fees,
direction
)
Get trade statistics.
gross_exposure_nb function¶
gross_exposure_nb(
asset_value,
cash
)
Get gross exposure per column/group.
group_mean_reduce_nb function¶
group_mean_reduce_nb(
group,
a
)
Mean reducer for grouped columns.
i_group_any_reduce_nb function¶
i_group_any_reduce_nb(
i,
group,
a
)
Boolean "any" reducer for grouped columns.
init_cash_grouped_nb function¶
init_cash_grouped_nb(
init_cash,
group_lens,
cash_sharing
)
Get initial cash per group.
init_cash_nb function¶
init_cash_nb(
init_cash,
group_lens,
cash_sharing
)
Get initial cash per column.
init_records_nb function¶
init_records_nb(
target_shape,
max_orders=None,
max_logs=0
)
Initialize order and log records.
is_grouped_nb function¶
is_grouped_nb(
group_lens
)
Check if columm,ns are grouped, that is, more than one column per group.
ls_enex_signal_func_nb function¶
ls_enex_signal_func_nb(
c,
long_entries,
long_exits,
short_entries,
short_exits
)
Get an element of direction-aware signals.
no_adjust_sl_func_nb function¶
no_adjust_sl_func_nb(
c,
*args
)
Placeholder function that returns the initial stop-loss value and trailing flag.
no_adjust_tp_func_nb function¶
no_adjust_tp_func_nb(
c,
*args
)
Placeholder function that returns the initial take-profit value.
no_flex_order_func_nb function¶
no_flex_order_func_nb(
c,
*args
)
Placeholder flexible order function that returns break column and no order.
no_order_func_nb function¶
no_order_func_nb(
c,
*args
)
Placeholder order function that returns no order.
no_post_func_nb function¶
no_post_func_nb(
c,
*args
)
Placeholder postprocessing function that returns nothing.
no_pre_func_nb function¶
no_pre_func_nb(
c,
*args
)
Placeholder preprocessing function that forwards received arguments down the stack.
no_signal_func_nb function¶
no_signal_func_nb(
c,
*args
)
Placeholder signal function that returns no signal.
order_nb function¶
order_nb(
size=nan,
price=inf,
size_type=0,
direction=2,
fees=0.0,
fixed_fees=0.0,
slippage=0.0,
min_size=0.0,
max_size=inf,
size_granularity=nan,
reject_prob=0.0,
lock_cash=False,
allow_partial=True,
raise_reject=False,
log=False
)
Create an order.
See Order for details on arguments.
order_not_filled_nb function¶
order_not_filled_nb(
status,
status_info
)
Return OrderResult for order that hasn't been filled.
order_nothing_nb function¶
order_nothing_nb()
Convenience function to order nothing.
position_coverage_grouped_nb function¶
position_coverage_grouped_nb(
position_mask,
group_lens
)
Get coverage of position for each row and group.
position_mask_grouped_nb function¶
position_mask_grouped_nb(
position_mask,
group_lens
)
Get whether in position for each row and group.
process_order_nb function¶
process_order_nb(
i,
col,
group,
state,
update_value,
order,
order_records,
log_records
)
Process an order by executing it, saving relevant information to the logs, and returning a new state.
raise_rejected_order_nb function¶
raise_rejected_order_nb(
order_result
)
Raise an RejectedOrderError.
replace_inf_price_nb function¶
replace_inf_price_nb(
prev_close,
close,
order
)
Replace infinity price in an order.
require_call_seq function¶
require_call_seq(
call_seq
)
Force the call sequence array to pass our requirements.
resolve_dir_conflict_nb function¶
resolve_dir_conflict_nb(
position_now,
is_long_entry,
is_short_entry,
upon_dir_conflict
)
Resolve any direction conflict between a long entry and a short entry.
resolve_opposite_entry_nb function¶
resolve_opposite_entry_nb(
position_now,
is_long_entry,
is_long_exit,
is_short_entry,
is_short_exit,
upon_opposite_entry,
accumulate
)
Resolve opposite entry.
resolve_signal_conflict_nb function¶
resolve_signal_conflict_nb(
position_now,
is_entry,
is_exit,
direction,
conflict_mode
)
Resolve any conflict between an entry and an exit.
resolve_stop_price_and_slippage_nb function¶
resolve_stop_price_and_slippage_nb(
stop_price,
price,
close,
slippage,
stop_exit_price
)
Resolve price and slippage of a stop order.
returns_in_sim_order_nb function¶
returns_in_sim_order_nb(
value_iso,
group_lens,
init_cash_grouped,
call_seq
)
Get portfolio return series in simulation order.
sell_nb function¶
sell_nb(
exec_state,
size,
price,
direction=2,
fees=0.0,
fixed_fees=0.0,
slippage=0.0,
min_size=0.0,
max_size=inf,
size_granularity=nan,
lock_cash=False,
allow_partial=True,
percent=nan
)
Sell or/and short sell.
should_update_stop_nb function¶
should_update_stop_nb(
stop,
upon_stop_update
)
Whether to update stop.
shuffle_call_seq_nb function¶
shuffle_call_seq_nb(
call_seq,
group_lens
)
Shuffle the call sequence array.
signals_to_size_nb function¶
signals_to_size_nb(
position_now,
is_long_entry,
is_long_exit,
is_short_entry,
is_short_exit,
size,
size_type,
accumulate,
val_price_now
)
Translate direction-aware signals into size, size type, and direction.
simulate_from_orders_nb function¶
simulate_from_orders_nb(
target_shape,
group_lens,
init_cash,
call_seq,
size=array(inf),
price=array(inf),
size_type=array(0),
direction=array(2),
fees=array(0.),
fixed_fees=array(0.),
slippage=array(0.),
min_size=array(0.),
max_size=array(inf),
size_granularity=array(nan),
reject_prob=array(0.),
lock_cash=array(False),
allow_partial=array(True),
raise_reject=array(False),
log=array(False),
val_price=array(inf),
close=array(nan),
auto_call_seq=False,
ffill_val_price=True,
update_value=False,
max_orders=None,
max_logs=0,
flex_2d=True
)
Creates on order out of each element.
Iterates in the column-major order. Utilizes flexible broadcasting.
Note
Should be only grouped if cash sharing is enabled.
If auto_call_seq is True, make sure that call_seq follows CallSeqType.Default.
Single value should be passed as a 0-dim array (for example, by using np.asarray(value)).
Usage
- Buy and hold using all cash and closing price (default):
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from vectorbt.records.nb import col_map_nb
>>> from vectorbt.portfolio.nb import simulate_from_orders_nb, asset_flow_nb
>>> from vectorbt.portfolio.enums import Direction
>>> close = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])[:, None]
>>> order_records, _ = simulate_from_orders_nb(
... target_shape=close.shape,
... close=close,
... group_lens=np.array([1]),
... init_cash=np.array([100]),
... call_seq=np.full(close.shape, 0)
... )
>>> col_map = col_map_nb(order_records['col'], close.shape[1])
>>> asset_flow = asset_flow_nb(close.shape, order_records, col_map, Direction.Both)
>>> asset_flow
array([[100.],
[ 0.],
[ 0.],
[ 0.],
[ 0.]])
simulate_from_signal_func_nb function¶
simulate_from_signal_func_nb(
target_shape,
group_lens,
init_cash,
call_seq,
signal_func_nb=no_signal_func_nb,
signal_args=(),
size=array(inf),
price=array(inf),
size_type=array(0),
fees=array(0.),
fixed_fees=array(0.),
slippage=array(0.),
min_size=array(0.),
max_size=array(inf),
size_granularity=array(nan),
reject_prob=array(0.),
lock_cash=array(False),
allow_partial=array(True),
raise_reject=array(False),
log=array(False),
accumulate=array(0),
upon_long_conflict=array(0),
upon_short_conflict=array(0),
upon_dir_conflict=array(0),
upon_opposite_entry=array(4),
val_price=array(inf),
open=array(nan),
high=array(nan),
low=array(nan),
close=array(nan),
sl_stop=array(nan),
sl_trail=array(False),
tp_stop=array(nan),
stop_entry_price=array(3),
stop_exit_price=array(0),
upon_stop_exit=array(0),
upon_stop_update=array(1),
adjust_sl_func_nb=no_adjust_sl_func_nb,
adjust_sl_args=(),
adjust_tp_func_nb=no_adjust_tp_func_nb,
adjust_tp_args=(),
use_stops=True,
auto_call_seq=False,
ffill_val_price=True,
update_value=False,
max_orders=None,
max_logs=0,
flex_2d=True
)
Creates an order out of each element by resolving entry and exit signals returned by signal_func_nb.
Iterates in the column-major order. Utilizes flexible broadcasting.
Signals are processed using the following pipeline:
1) If there is a stop signal, convert it to direction-aware signals and proceed to 7) 2) Get direction-aware signals using signal_func_nb 3) Resolve any entry and exit conflict of each direction using resolve_signal_conflict_nb() 4) Resolve any direction conflict using resolve_dir_conflict_nb() 5) Resolve an opposite entry signal scenario using resolve_opposite_entry_nb() 7) Convert the final signals into size, size type, and direction using signals_to_size_nb()
Note
Should be only grouped if cash sharing is enabled.
If auto_call_seq is True, make sure that call_seq follows CallSeqType.Default.
Single value should be passed as a 0-dim array (for example, by using np.asarray(value)).
Usage
- Buy and hold using all cash and closing price (default):
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from vectorbt.records.nb import col_map_nb
>>> from vectorbt.portfolio import nb
>>> from vectorbt.portfolio.enums import Direction
>>> close = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])[:, None]
>>> order_records, _ = nb.simulate_from_signal_func_nb(
... target_shape=close.shape,
... close=close,
... group_lens=np.array([1]),
... init_cash=np.array([100]),
... call_seq=np.full(close.shape, 0),
... signal_func_nb=nb.dir_enex_signal_func_nb,
... signal_args=(np.asarray(True), np.asarray(False), np.asarray(Direction.LongOnly))
... )
>>> col_map = col_map_nb(order_records['col'], close.shape[1])
>>> asset_flow = nb.asset_flow_nb(close.shape, order_records, col_map, Direction.Both)
>>> asset_flow
array([[100.],
[ 0.],
[ 0.],
[ 0.],
[ 0.]])
simulate_nb function¶
simulate_nb(
target_shape,
group_lens,
init_cash,
cash_sharing,
call_seq,
segment_mask=array(True),
call_pre_segment=False,
call_post_segment=False,
pre_sim_func_nb=no_pre_func_nb,
pre_sim_args=(),
post_sim_func_nb=no_post_func_nb,
post_sim_args=(),
pre_group_func_nb=no_pre_func_nb,
pre_group_args=(),
post_group_func_nb=no_post_func_nb,
post_group_args=(),
pre_segment_func_nb=no_pre_func_nb,
pre_segment_args=(),
post_segment_func_nb=no_post_func_nb,
post_segment_args=(),
order_func_nb=no_order_func_nb,
order_args=(),
post_order_func_nb=no_post_func_nb,
post_order_args=(),
close=array(nan),
ffill_val_price=True,
update_value=False,
fill_pos_record=True,
max_orders=None,
max_logs=0,
flex_2d=True
)
Fill order and log records by iterating over a shape and calling a range of user-defined functions.
Starting with initial cash init_cash, iterates over each group and column in target_shape, and for each data point, generates an order using order_func_nb. Tries then to fulfill that order. Upon success, updates the current state including the cash balance and the position.
Returns order records of layout order_dt and log records of layout log_dt.
As opposed to simulate_row_wise_nb(), order processing happens in column-major order. Column-major order means processing the entire column/group with all rows before moving to the next one. See Row- and column-major order.
Args
target_shape:tuple- See SimulationContext.target_shape.
group_lens:array_likeofint- See SimulationContext.group_lens.
init_cash:array_likeoffloat- See SimulationContext.init_cash.
cash_sharing:bool- See SimulationContext.cash_sharing.
call_seq:array_likeofint- See SimulationContext.call_seq.
segment_mask:array_likeofbool- See SimulationContext.segment_mask.
call_pre_segment:bool- See SimulationContext.call_pre_segment.
call_post_segment:bool- See SimulationContext.call_post_segment.
pre_sim_func_nb:callable-
Function called before simulation.
Can be used for creation of global arrays and setting the seed.
Should accept SimulationContext and
*pre_sim_args. Should return a tuple of any content, which is then passed topre_group_func_nbandpost_group_func_nb. pre_sim_args:tuple- Packed arguments passed to
pre_sim_func_nb. post_sim_func_nb:callable-
Function called after simulation.
Should accept SimulationContext and
*post_sim_args. Should return nothing. post_sim_args:tuple- Packed arguments passed to
post_sim_func_nb. pre_group_func_nb:callable-
Function called before each group.
Should accept GroupContext, unpacked tuple from
pre_sim_func_nb, and*pre_group_args. Should return a tuple of any content, which is then passed topre_segment_func_nbandpost_segment_func_nb. pre_group_args:tuple- Packed arguments passed to
pre_group_func_nb. post_group_func_nb:callable-
Function called after each group.
Should accept GroupContext, unpacked tuple from
pre_sim_func_nb, and*post_group_args. Should return nothing. post_group_args:tuple- Packed arguments passed to
post_group_func_nb. pre_segment_func_nb:callable-
Function called before each segment.
Called if
segment_maskorcall_pre_segmentis True.Should accept SegmentContext, unpacked tuple from
pre_group_func_nb, and*pre_segment_args. Should return a tuple of any content, which is then passed toorder_func_nbandpost_order_func_nb.This is the right place to change call sequence and set the valuation price. Group re-valuation and update of the open position stats happens right after this function, regardless of whether it has been called.
Note
To change the call sequence of a segment, access SegmentContext.call_seq_now and change it in-place. Make sure to not generate any new arrays as it may negatively impact performance. Assigning
SegmentContext.call_seq_nowas any other context (named tuple) value is not supported. See SegmentContext.call_seq_now.Note
You can override elements of
last_val_priceto manipulate group valuation. See SimulationContext.last_val_price. pre_segment_args:tuple- Packed arguments passed to
pre_segment_func_nb. post_segment_func_nb:callable-
Function called after each segment.
Called if
segment_maskorcall_post_segmentis True.The last group re-valuation and update of the open position stats happens right before this function, regardless of whether it has been called.
Should accept SegmentContext, unpacked tuple from
pre_group_func_nb, and*post_segment_args. Should return nothing. post_segment_args:tuple- Packed arguments passed to
post_segment_func_nb. order_func_nb:callable-
Order generation function.
Used for either generating an order or skipping.
Should accept OrderContext, unpacked tuple from
pre_segment_func_nb, and*order_args. Should return Order.Note
If the returned order has been rejected, there is no way of issuing a new order. You should make sure that the order passes, for example, by using try_order_nb().
To have a greater freedom in order management, use flex_simulate_nb().
order_args:tuple- Arguments passed to
order_func_nb. post_order_func_nb:callable-
Callback that is called after the order has been processed.
Used for checking the order status and doing some post-processing.
Should accept PostOrderContext, unpacked tuple from
pre_segment_func_nb, and*post_order_args. Should return nothing. post_order_args:tuple- Arguments passed to
post_order_func_nb. close:array_likeoffloat- See SimulationContext.close.
ffill_val_price:bool- See SimulationContext.ffill_val_price.
update_value:bool- See SimulationContext.update_value.
fill_pos_record:bool- See SimulationContext.fill_pos_record.
max_orders:int- Size of the order records array.
max_logs:int- Size of the log records array.
flex_2d:bool- See SimulationContext.flex_2d.
Note
Remember that indexing of 2-dim arrays in vectorbt follows that of pandas: a[i, col].
Warning
You can only safely access data of columns that are to the left of the current group and rows that are to the top of the current row within the same group. Other data points have not been processed yet and thus empty. Accessing them will not trigger any errors or warnings, but provide you with arbitrary data (see np.empty).
Call hierarchy
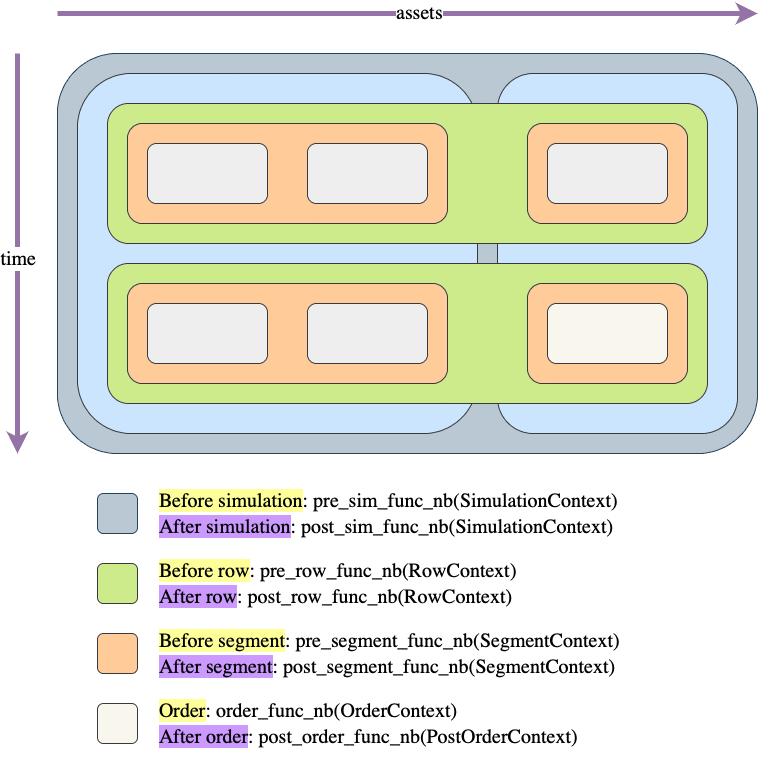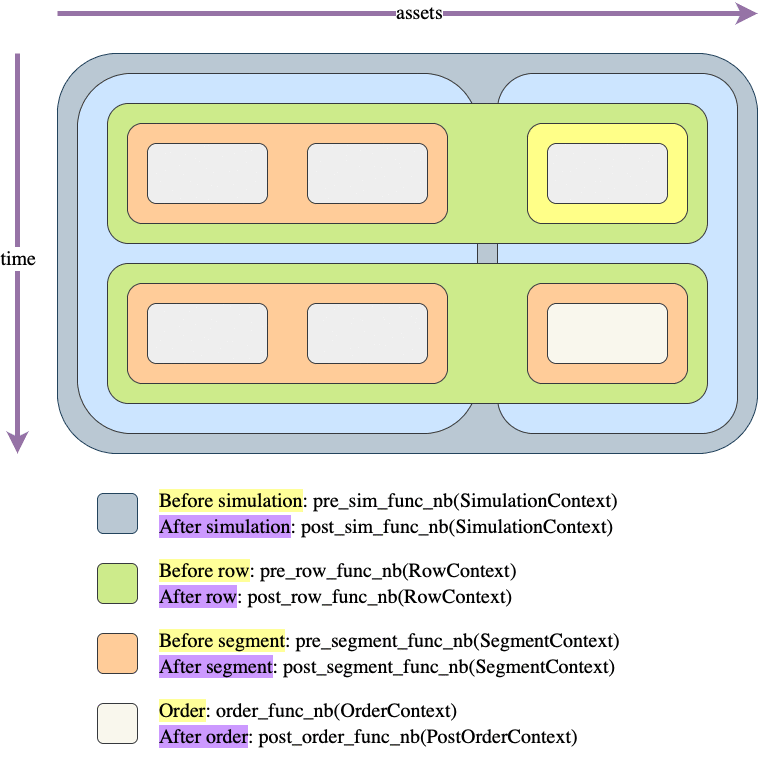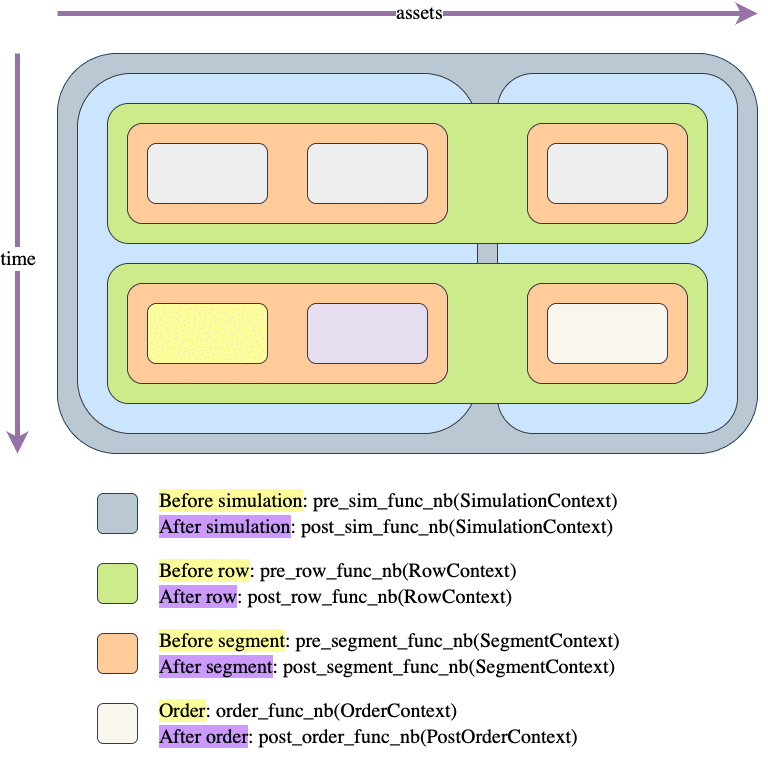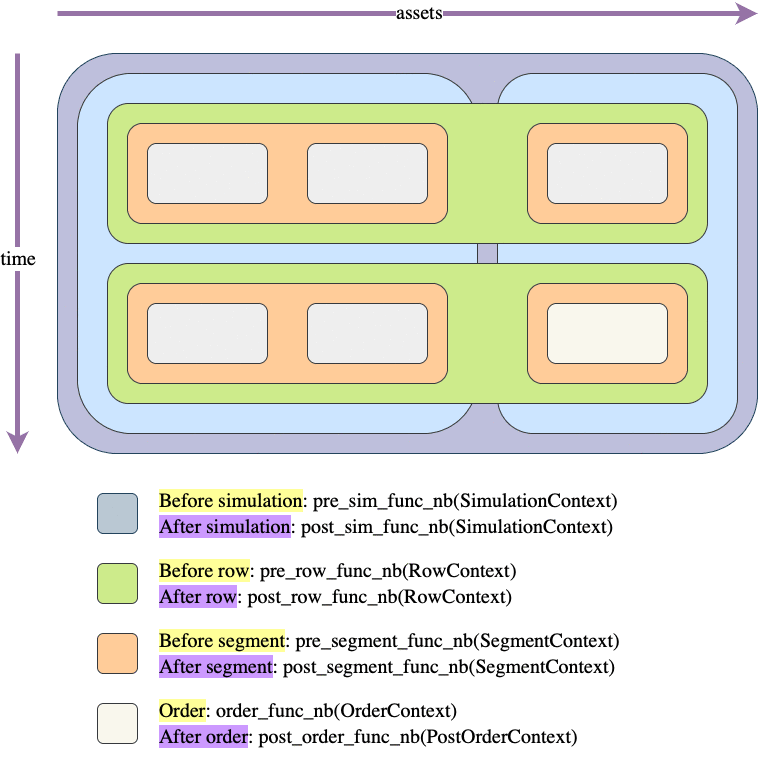
Like most things in the vectorbt universe, simulation is also done by iterating over a (imaginary) frame. This frame consists of two dimensions: time (rows) and assets/features (columns). Each element of this frame is a potential order, which gets generated by calling an order function.
The question is: how do we move across this frame to simulate trading? There are two movement patterns: column-major (as done by simulate_nb()) and row-major order (as done by simulate_row_wise_nb()). In each of these patterns, we are always moving from top to bottom (time axis) and from left to right (asset/feature axis); the only difference between them is across which axis we are moving faster: do we want to process each column first (thus assuming that columns are independent) or each row? Choosing between them is mostly a matter of preference, but it also makes different data being available when generating an order.
The frame is further divided into "blocks": columns, groups, rows, segments, and elements. For example, columns can be grouped into groups that may or may not share the same capital. Regardless of capital sharing, each collection of elements within a group and a time step is called a segment, which simply defines a single context (such as shared capital) for one or multiple orders. Each segment can also define a custom sequence (a so-called call sequence) in which orders are executed.
You can imagine each of these blocks as a rectangle drawn over different parts of the frame, and having its own context and pre/post-processing function. The pre-processing function is a simple callback that is called before entering the block, and can be provided by the user to, for example, prepare arrays or do some custom calculations. It must return a tuple (can be empty) that is then unpacked and passed as arguments to the pre- and postprocessing function coming next in the call hierarchy. The postprocessing function can be used, for example, to write user-defined arrays such as returns.
Let's demonstrate a frame with one group of two columns and one group of one column, and the following call sequence:
array([[0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0]])
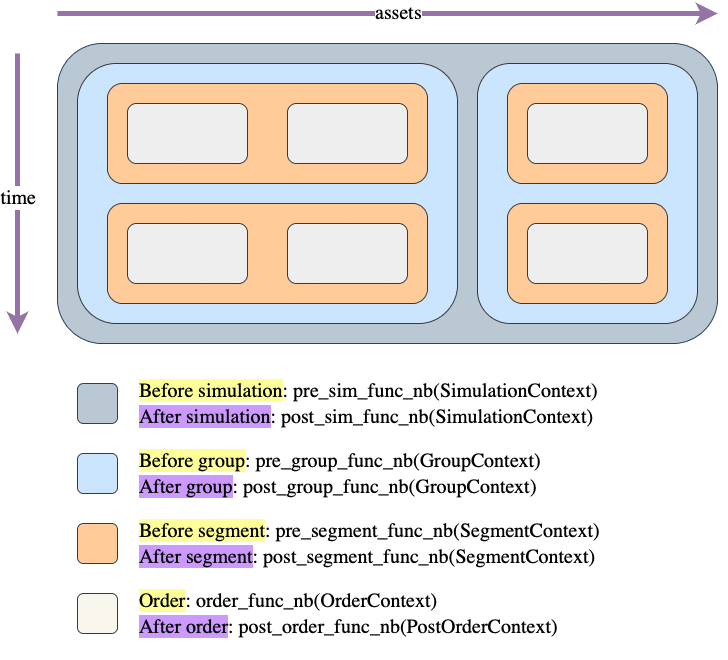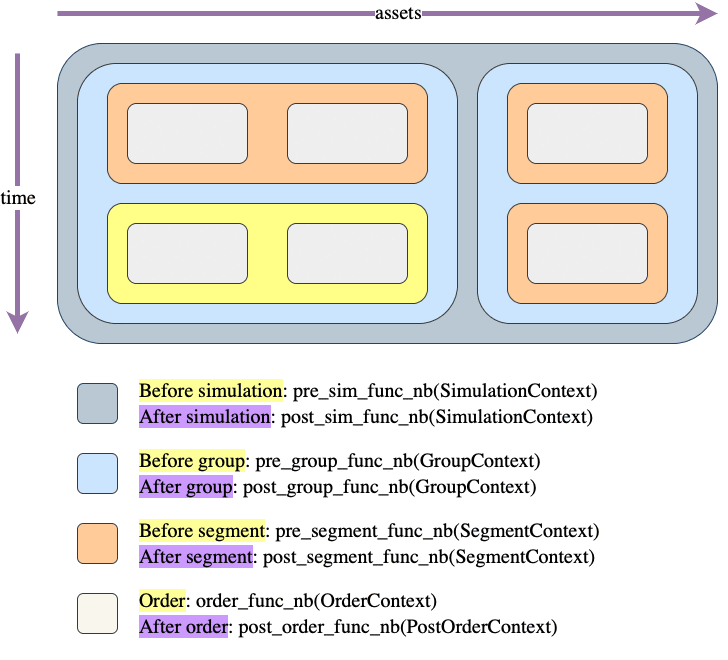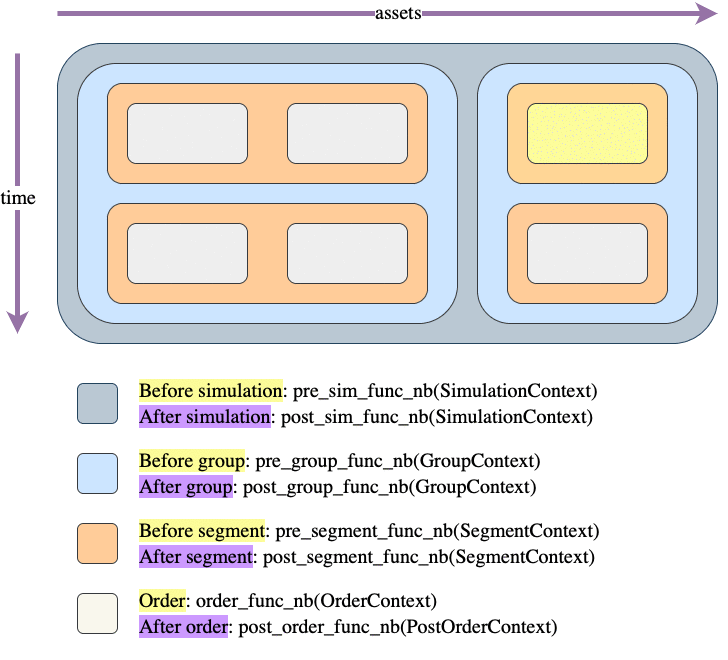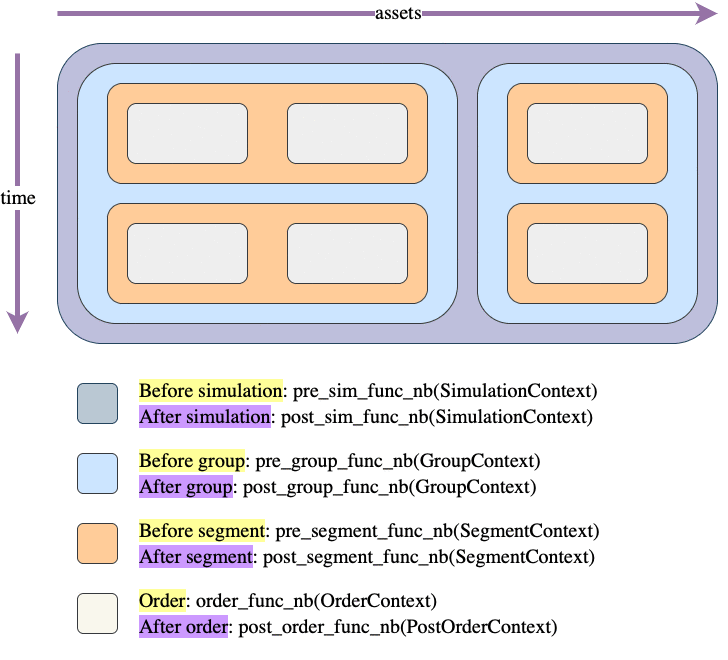
And here is the context information available at each step:
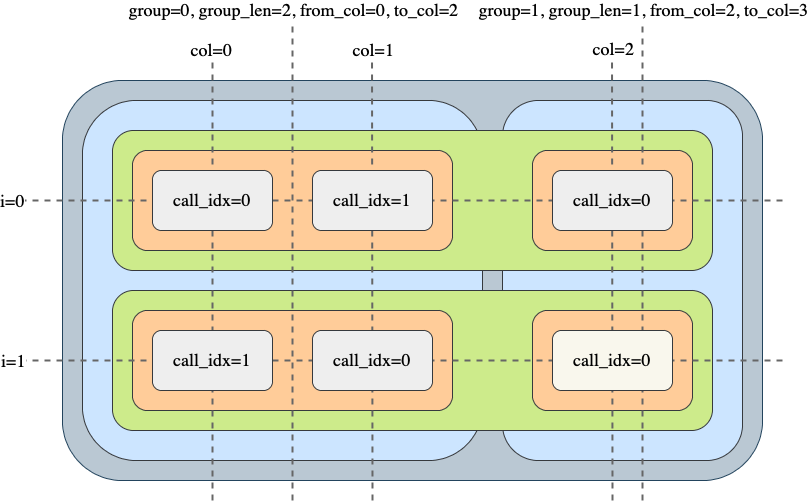
Usage
- Create a group of three assets together sharing 100$ and simulate an equal-weighted portfolio that rebalances every second tick, all without leaving Numba:
>>> import numpy as np
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> from collections import namedtuple
>>> from numba import njit
>>> from vectorbt.generic.plotting import Scatter
>>> from vectorbt.records.nb import col_map_nb
>>> from vectorbt.portfolio.enums import SizeType, Direction
>>> from vectorbt.portfolio.nb import (
... get_col_elem_nb,
... get_elem_nb,
... order_nb,
... simulate_nb,
... simulate_row_wise_nb,
... build_call_seq,
... sort_call_seq_nb,
... asset_flow_nb,
... assets_nb,
... asset_value_nb
... )
>>> @njit
... def pre_sim_func_nb(c):
... print('before simulation')
... # Create a temporary array and pass it down the stack
... order_value_out = np.empty(c.target_shape[1], dtype=np.float64)
... return (order_value_out,)
>>> @njit
... def pre_group_func_nb(c, order_value_out):
... print('\tbefore group', c.group)
... # Forward down the stack (you can omit pre_group_func_nb entirely)
... return (order_value_out,)
>>> @njit
... def pre_segment_func_nb(c, order_value_out, size, price, size_type, direction):
... print('\t\tbefore segment', c.i)
... for col in range(c.from_col, c.to_col):
... # Here we use order price for group valuation
... c.last_val_price[col] = get_col_elem_nb(c, col, price)
...
... # Reorder call sequence of this segment such that selling orders come first and buying last
... # Rearranges c.call_seq_now based on order value (size, size_type, direction, and val_price)
... # Utilizes flexible indexing using get_col_elem_nb (as we did above)
... sort_call_seq_nb(c, size, size_type, direction, order_value_out[c.from_col:c.to_col])
... # Forward nothing
... return ()
>>> @njit
... def order_func_nb(c, size, price, size_type, direction, fees, fixed_fees, slippage):
... print('\t\t\tcreating order', c.call_idx, 'at column', c.col)
... # Create and return an order
... return order_nb(
... size=get_elem_nb(c, size),
... price=get_elem_nb(c, price),
... size_type=get_elem_nb(c, size_type),
... direction=get_elem_nb(c, direction),
... fees=get_elem_nb(c, fees),
... fixed_fees=get_elem_nb(c, fixed_fees),
... slippage=get_elem_nb(c, slippage)
... )
>>> @njit
... def post_order_func_nb(c):
... print('\t\t\t\torder status:', c.order_result.status)
... return None
>>> @njit
... def post_segment_func_nb(c, order_value_out):
... print('\t\tafter segment', c.i)
... return None
>>> @njit
... def post_group_func_nb(c, order_value_out):
... print('\tafter group', c.group)
... return None
>>> @njit
... def post_sim_func_nb(c):
... print('after simulation')
... return None
>>> target_shape = (5, 3)
>>> np.random.seed(42)
>>> group_lens = np.array([3]) # one group of three columns
>>> init_cash = np.array([100.]) # one capital per group
>>> cash_sharing = True
>>> call_seq = build_call_seq(target_shape, group_lens) # will be overridden
>>> segment_mask = np.array([True, False, True, False, True])[:, None]
>>> segment_mask = np.copy(np.broadcast_to(segment_mask, target_shape))
>>> size = np.asarray(1 / target_shape[1]) # scalars must become 0-dim arrays
>>> price = close = np.random.uniform(1, 10, size=target_shape)
>>> size_type = np.asarray(SizeType.TargetPercent)
>>> direction = np.asarray(Direction.LongOnly)
>>> fees = np.asarray(0.001)
>>> fixed_fees = np.asarray(1.)
>>> slippage = np.asarray(0.001)
>>> order_records, log_records = simulate_nb(
... target_shape,
... group_lens,
... init_cash,
... cash_sharing,
... call_seq,
... segment_mask=segment_mask,
... pre_sim_func_nb=pre_sim_func_nb,
... post_sim_func_nb=post_sim_func_nb,
... pre_group_func_nb=pre_group_func_nb,
... post_group_func_nb=post_group_func_nb,
... pre_segment_func_nb=pre_segment_func_nb,
... pre_segment_args=(size, price, size_type, direction),
... post_segment_func_nb=post_segment_func_nb,
... order_func_nb=order_func_nb,
... order_args=(size, price, size_type, direction, fees, fixed_fees, slippage),
... post_order_func_nb=post_order_func_nb
... )
before simulation
before group 0
before segment 0
creating order 0 at column 0
order status: 0
creating order 1 at column 1
order status: 0
creating order 2 at column 2
order status: 0
after segment 0
before segment 2
creating order 0 at column 1
order status: 0
creating order 1 at column 2
order status: 0
creating order 2 at column 0
order status: 0
after segment 2
before segment 4
creating order 0 at column 0
order status: 0
creating order 1 at column 2
order status: 0
creating order 2 at column 1
order status: 0
after segment 4
after group 0
after simulation
>>> pd.DataFrame.from_records(order_records)
id col idx size price fees side
0 0 0 0 7.626262 4.375232 1.033367 0
1 1 1 0 3.488053 9.565985 1.033367 0
2 2 2 0 3.972040 7.595533 1.030170 0
3 3 1 2 0.920352 8.786790 1.008087 1
4 4 2 2 0.448747 6.403625 1.002874 1
5 5 0 2 5.210115 1.524275 1.007942 0
6 6 0 4 7.899568 8.483492 1.067016 1
7 7 2 4 12.378281 2.639061 1.032667 0
8 8 1 4 10.713236 2.913963 1.031218 0
>>> call_seq
array([[0, 1, 2],
[0, 1, 2],
[1, 2, 0],
[0, 1, 2],
[0, 2, 1]])
>>> col_map = col_map_nb(order_records['col'], target_shape[1])
>>> asset_flow = asset_flow_nb(target_shape, order_records, col_map, Direction.Both)
>>> assets = assets_nb(asset_flow)
>>> asset_value = asset_value_nb(close, assets)
>>> Scatter(data=asset_value).fig.show()
Note that the last order in a group with cash sharing is always disadvantaged as it has a bit less funds than the previous orders due to costs, which are not included when valuating the group.
simulate_row_wise_nb function¶
simulate_row_wise_nb(
target_shape,
group_lens,
init_cash,
cash_sharing,
call_seq,
segment_mask=array(True),
call_pre_segment=False,
call_post_segment=False,
pre_sim_func_nb=no_pre_func_nb,
pre_sim_args=(),
post_sim_func_nb=no_post_func_nb,
post_sim_args=(),
pre_row_func_nb=no_pre_func_nb,
pre_row_args=(),
post_row_func_nb=no_post_func_nb,
post_row_args=(),
pre_segment_func_nb=no_pre_func_nb,
pre_segment_args=(),
post_segment_func_nb=no_post_func_nb,
post_segment_args=(),
order_func_nb=no_order_func_nb,
order_args=(),
post_order_func_nb=no_post_func_nb,
post_order_args=(),
close=array(nan),
ffill_val_price=True,
update_value=False,
fill_pos_record=True,
max_orders=None,
max_logs=0,
flex_2d=True
)
Same as simulate_nb(), but iterates in row-major order.
Row-major order means processing the entire row with all groups/columns before moving to the next one.
The main difference is that instead of pre_group_func_nb it now exposes pre_row_func_nb, which is executed per entire row. It should accept RowContext.
Note
Function pre_row_func_nb is only called if there is at least on active segment in the row. Functions pre_segment_func_nb and order_func_nb are only called if their segment is active. If the main task of pre_row_func_nb is to activate/deactivate segments, all segments should be activated by default to allow pre_row_func_nb to be called.
Warning
You can only safely access data points that are to the left of the current group and rows that are to the top of the current row.
Call hierarchy
Let's illustrate the same example as in simulate_nb() but adapted for this function:
Usage
- Running the same example as in simulate_nb() but adapted for this function:
>>> @njit
... def pre_row_func_nb(c, order_value_out):
... print('\tbefore row', c.i)
... # Forward down the stack
... return (order_value_out,)
>>> @njit
... def post_row_func_nb(c, order_value_out):
... print('\tafter row', c.i)
... return None
>>> call_seq = build_call_seq(target_shape, group_lens)
>>> order_records, log_records = simulate_row_wise_nb(
... target_shape,
... group_lens,
... init_cash,
... cash_sharing,
... call_seq,
... segment_mask=segment_mask,
... pre_sim_func_nb=pre_sim_func_nb,
... post_sim_func_nb=post_sim_func_nb,
... pre_row_func_nb=pre_row_func_nb,
... post_row_func_nb=post_row_func_nb,
... pre_segment_func_nb=pre_segment_func_nb,
... pre_segment_args=(size, price, size_type, direction),
... post_segment_func_nb=post_segment_func_nb,
... order_func_nb=order_func_nb,
... order_args=(size, price, size_type, direction, fees, fixed_fees, slippage),
... post_order_func_nb=post_order_func_nb
... )
before simulation
before row 0
before segment 0
creating order 0 at column 0
order status: 0
creating order 1 at column 1
order status: 0
creating order 2 at column 2
order status: 0
after segment 0
after row 0
before row 1
after row 1
before row 2
before segment 2
creating order 0 at column 1
order status: 0
creating order 1 at column 2
order status: 0
creating order 2 at column 0
order status: 0
after segment 2
after row 2
before row 3
after row 3
before row 4
before segment 4
creating order 0 at column 0
order status: 0
creating order 1 at column 2
order status: 0
creating order 2 at column 1
order status: 0
after segment 4
after row 4
after simulation
sort_call_seq_nb function¶
sort_call_seq_nb(
ctx,
size,
size_type,
direction,
order_value_out,
ctx_select=True
)
Sort call sequence attached to SegmentContext.
Note
Can only be used in non-flexible simulation functions.
sort_call_seq_out_nb function¶
sort_call_seq_out_nb(
ctx,
size,
size_type,
direction,
order_value_out,
call_seq_out,
ctx_select=True
)
Sort call sequence call_seq_out based on the value of each potential order.
Accepts SegmentContext and other arguments, sorts call_seq_out in place, and returns nothing.
Arrays size, size_type, and direction utilize flexible indexing. If ctx_select is True, selects the elements of each size, size_type, and direction using get_col_elem_nb() assuming that each array can broadcast to target_shape. Otherwise, selects using flex_select_auto_nb() assuming that each array can broadcast to group_len.
The lengths of order_value_out and call_seq_out should match the number of columns in the group. Array order_value_out should be empty and will contain sorted order values after execution. Array call_seq_out should be filled with integers ranging from 0 to the number of columns in the group (in this exact order).
Best called once from pre_segment_func_nb.
Note
Cash sharing must be enabled and call_seq_out should follow CallSeqType.Default.
Should be used in flexible simulation functions.
sum_grouped_nb function¶
sum_grouped_nb(
a,
group_lens
)
Squeeze each group of columns into a single column using sum operation.
total_benchmark_return_nb function¶
total_benchmark_return_nb(
benchmark_value
)
Get total market return per column/group.
total_profit_grouped_nb function¶
total_profit_grouped_nb(
total_profit,
group_lens
)
Get total profit per group.
total_profit_nb function¶
total_profit_nb(
target_shape,
close,
order_records,
col_map
)
Get total profit per column.
A much faster version than the one based on value_nb().
total_return_nb function¶
total_return_nb(
total_profit,
init_cash
)
Get total return per column/group.
trade_losing_streak_nb function¶
trade_losing_streak_nb(
records
)
Return the current losing streak of each trade.
trade_winning_streak_nb function¶
trade_winning_streak_nb(
records
)
Return the current winning streak of each trade.
try_order_nb function¶
try_order_nb(
ctx,
order
)
Execute an order without persistence.
update_open_pos_stats_nb function¶
update_open_pos_stats_nb(
record,
position_now,
price
)
Update statistics of an open position record using custom price.
update_pos_record_nb function¶
update_pos_record_nb(
record,
i,
col,
position_before,
position_now,
order_result
)
Update position record after filling an order.
update_value_nb function¶
update_value_nb(
cash_before,
cash_now,
position_before,
position_now,
val_price_before,
price,
value_before
)
Update valuation price and value.
value_in_sim_order_nb function¶
value_in_sim_order_nb(
cash,
asset_value,
group_lens,
call_seq
)
Get portfolio value series in simulation order.
value_nb function¶
value_nb(
cash,
asset_value
)
Get portfolio value series per column/group.
